
Content Menu
● How Activated Carbon Adsorption Works
● What Do Activated Carbon Filters Remove?
● Do Activated Carbon Filters Work for Water Treatment?
● Do Activated Carbon Filters Work for Air and Gas?
● Factors That Affect Activated Carbon Filter Performance
● Industrial Uses of Activated Carbon Filters
● Conclusion
● FAQs About Activated Carbon Filters
>> 1. How long do activated carbon filters last?
>> 2. Do activated carbon filters remove all contaminants?
>> 3. Is activated carbon safe for drinking water and food applications?
>> 4. Can activated carbon be regenerated or reused?
>> 5. Do activated carbon air filters replace HEPA filters?
● Citations:
Do activated carbon filters work? Yes, activated carbon filters work very effectively for removing many dissolved chemicals, odors, colors, and volatile contaminants from water, air, and gas, especially when correctly selected and maintained for the target application. However, no single activated carbon filter removes all contaminants, so system design and carbon choice are critical for real performance.[1][2][3][4]
Activated carbon is a highly porous adsorbent material produced from carbon-rich raw materials such as coal, coconut shells, wood, or nutshells that are “activated” to create millions of micro‑ and mesopores. These pores give activated carbon an extremely large internal surface area, often exceeding 1,000 m² per gram, which is the basis of its filtration performance.[5][6][2]
In both water and air systems, activated carbon filters work through adsorption, where contaminants adhere to the surface of the activated carbon rather than being absorbed into its bulk. As contaminated fluid (water, air, or gas) passes through the activated carbon bed, molecules such as chlorine, VOCs, odors, and many organics are trapped inside the pores and removed from the stream.[7][8][6][1]

How Activated Carbon Adsorption Works
Activated carbon filtration is governed by physical and sometimes chemical forces that drive molecules from the fluid phase onto the activated carbon surface. The huge surface area, pore size distribution, and surface chemistry of the activated carbon determine which contaminants are captured and how strongly they are held.[6][2][5]
- Adsorption vs absorption
- Adsorption: contaminants stick to the outer and inner surfaces of activated carbon pores due to van der Waals forces or specific chemical interactions.[7][6]
- Absorption: a substance is taken into the volume of a material, like water into a sponge, which is not how activated carbon primarily functions.[8][7]
- Physisorption and chemisorption
- Physisorption is controlled by weak forces and is common for VOCs and many organic compounds on activated carbon filters in air systems.[9][6]
- Chemisorption involves stronger chemical bonds and is used in some impregnated activated carbon grades for specific gases, such as acid gases or ammonia.[10][6]
Over time, as the pores of the activated carbon fill up, the adsorption sites become occupied and the filter approaches breakthrough, where contaminants begin to pass through again. At this stage, the activated carbon must be replaced or thermally reactivated to restore its adsorption capacity.[3][4][5]
What Do Activated Carbon Filters Remove?
Activated carbon filters remove a wide spectrum of organic and some inorganic contaminants, but performance always depends on carbon type, contact time, and system design. In practice, activated carbon is extremely effective for many taste, odor, and color problems and widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial systems.[2][5][1][3]
- Common water contaminants removed by activated carbon
- Chlorine and chlorinated by‑products, which significantly improves taste and odor of drinking water.[11][4]
- Volatile organic compounds (VOCs), pesticides, herbicides, and many industrial organics.[1][3]
- Organic color bodies and some synthetic dyes in process liquids.[12][5]
- Common air and gas contaminants removed by activated carbon
- VOCs and chemical fumes from industrial processes or building materials.[13][10]
- Odors from food processing, waste treatment, smoking, or solvents.[10][1]
- Certain toxic gases such as sulfur compounds, some acid gases, and specific vapors when appropriate impregnated activated carbon is used.[14][10]
Some substances are only partially removed by standard activated carbon filters, or require specially engineered activated carbon media or combined technologies. For example, certain heavy metals, PFAS, and micro‑pollutants need high‑performance activated carbon grades, long contact times, or integration with ion exchange, membranes, or other processes.[15][11][2]
Do Activated Carbon Filters Work for Water Treatment?
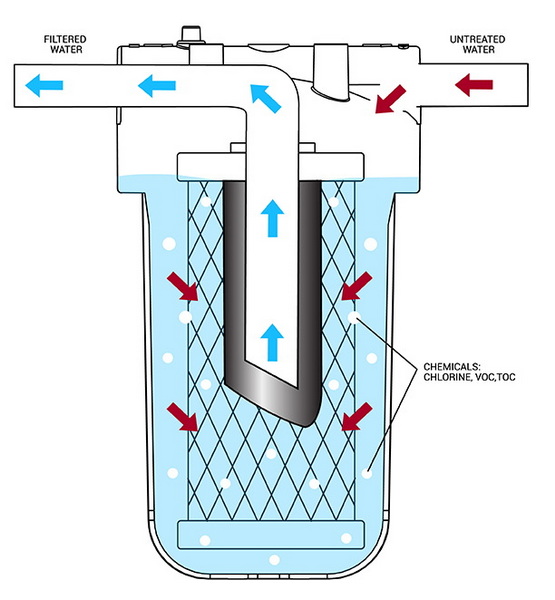
In water treatment, activated carbon filters are among the most widely used technologies for polishing municipal, industrial, and process water before use or discharge. Granular activated carbon (GAC) and powdered activated carbon (PAC) are employed in filters, columns, and batch systems at a range of scales, from household pitchers to large industrial plants.[5][2][12][3]
- Key functions of activated carbon in water
- Removal of chlorine and chloramines to protect downstream membranes and improve water taste.[11][3]
- Adsorption of organics, including VOCs, phenols, disinfection by‑products, and many odor‑causing compounds.[2][1]
- Decolorization and polishing of beverages, syrups, and process streams in food and beverage production.[12][5]
- Industrial applications of activated carbon water filters
- Food & beverage: activated carbon filters improve product flavor, color, and stability in soft drinks, beer, juices, and bottled water.[5][12]
- Pharmaceutical: activated carbon is used to meet strict water quality standards and remove trace organic impurities from feed water and intermediates.[12][5]
- Chemical & petrochemical: activated carbon filters process water and wastewater to remove organic contaminants, residual solvents, and COD.[5][12]
However, activated carbon cannot remove all dissolved inorganic ions such as hardness, nitrate, or most simple metal cations at significant levels, so many systems pair activated carbon filters with softeners, RO, or ion exchange. Properly sized activated carbon beds, adequate empty bed contact time (EBCT), and regular carbon replacement schedules are essential to maintain performance in continuous operation.[4][3][2]
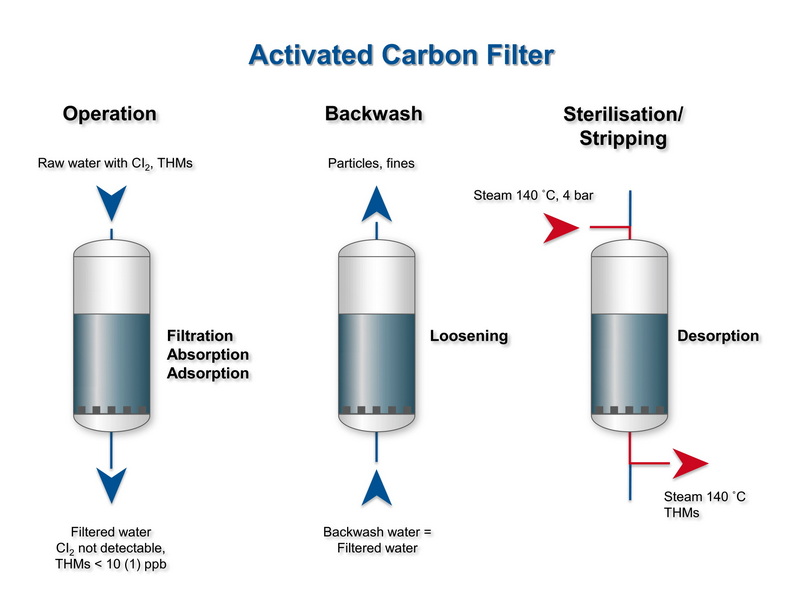
Do Activated Carbon Filters Work for Air and Gas?
Activated carbon is a core technology in air and gas purification because it captures gas‑phase contaminants that particulate filters (like HEPA) cannot remove. In these applications, air or gas is blown through a bed or cartridge of activated carbon, often combined with pre‑filters for dust and post‑filters for fine particles.[16][9][13]
- How activated carbon air filters work
- Contaminated air carrying VOCs, odors, and gaseous pollutants passes through an activated carbon bed, where molecules adsorb onto the large internal surface.[9][7]
- The porous activated carbon structure allows deep penetration of gases, so contaminants are trapped throughout the bed, not only on the outer surface.[13][6]
- Typical air and gas applications of activated carbon
- Industrial exhaust: activated carbon systems remove solvents, hydrocarbons, and odorous compounds in coating, printing, chemical, and petrochemical plants.[14][10]
- Indoor air quality: activated carbon filters in air purifiers capture VOCs and odors from household products, cooking, and smoking to improve comfort and health.[17][13]
- Special protection: impregnated activated carbon is used in respirators, safety cabinets, and lab fume hoods to control specific toxic gases.[6][14]
For particles such as dust, pollen, and microbes, activated carbon must be paired with HEPA or other mechanical filters, since activated carbon primarily handles gas‑phase contaminants rather than particulates. Correct sizing of the activated carbon filter, airflow rate, and pressure drop are also important to ensure real‑world efficiency in industrial air treatment systems.[17][13][10][14]
Factors That Affect Activated Carbon Filter Performance
The effectiveness of any activated carbon filter depends on matching the activated carbon to the application, then operating within the correct design envelope. Even high‑quality activated carbon will perform poorly if bed depth, contact time, or maintenance are inadequate.[3][4][2][12]
- Type and grade of activated carbon
- Different raw materials (coconut shell, coal, wood) and activation methods produce different pore structures and surface chemistries for activated carbon.[2][5]
- For example, some activated carbon grades are optimized for chlorine removal, others for organics or metal‑bearing species, so selection must match the target contaminants.[4][2]
- Particle size and bed design
- Smaller activated carbon particles generally provide higher adsorption rates due to larger external surface area, but cause higher pressure drop.[4][2]
- Sufficient bed depth and contact time (EBCT) are critical; shallow beds of activated carbon may not allow complete adsorption at high flow rates.[3][2]
- Operating conditions and maintenance
- Temperature, pH, and competing contaminants affect adsorption equilibria and must be considered when choosing an activated carbon solution.[2][5]
- As activated carbon becomes saturated, breakthrough occurs, so routine monitoring and scheduled replacement or reactivation are necessary for consistent performance.[3][4]
Industrial Uses of Activated Carbon Filters
Industrial users rely on activated carbon filters because they provide high‑efficiency removal of many contaminants with relatively low energy consumption and simple operation. Activated carbon filters are also considered eco‑friendly since activated carbon can be reactivated and reused in many cases, reducing waste and lifecycle cost.[11][12][5]
- Key industrial sectors using activated carbon filters
- Drinking water and municipal treatment: activated carbon removes chlorine, organics, and taste/odor compounds in centralized plants and point‑of‑use systems.[16][5]
- Power and environmental: activated carbon captures pollutants from flue gas and treats landfill gas or off‑gas streams for VOCs and odors.[16][5]
- Precious metal recovery and chemicals: activated carbon is used to adsorb gold and other metals from leach solutions and to purify process liquids.[16][5]
- Advantages of industrial activated carbon filtration
- Chemical‑free operation: activated carbon filters remove contaminants without dosing additional chemicals into the treated stream.[12][3]
- Versatility: a single activated carbon system can treat a wide range of organics and odors, and is easy to integrate with other unit operations.[1][12]
Because every industrial process is different, many plants order customized activated carbon grades and tailor filter design, bed depth, and contact time to their specific water, air, or gas quality targets. This customization ensures that activated carbon filtration remains cost‑effective while meeting regulatory and product‑quality requirements in sectors such as food & beverage, pharma, and chemicals.[5][12]
Conclusion
Activated carbon filters clearly work and have become a standard technology for water, air, and gas purification across residential, commercial, and industrial markets. By using highly porous activated carbon media, these filters adsorb chlorine, VOCs, odors, colors, and many organic contaminants, dramatically improving water taste, air quality, and process reliability.[8][1][5]
However, no activated carbon filter is universal; performance depends on matching activated carbon type, filter design, and operating conditions to the specific contaminants and quality targets. When properly engineered and maintained, activated carbon filters deliver reliable, cost‑effective, and sustainable purification for applications from drinking water and food production to chemical processing and industrial emission control.[4][2][12][5]
FAQs About Activated Carbon Filters
1. How long do activated carbon filters last?
The service life of an activated carbon filter depends on contaminant load, flow rate, and the amount of activated carbon in the cartridge or bed. In practice, small point‑of‑use activated carbon filters may need replacement every few months, while large industrial activated carbon beds can operate for many months or longer before breakthrough.[3][4]
2. Do activated carbon filters remove all contaminants?
No, activated carbon filters do not remove all contaminants, and performance varies by carbon type and system design. Activated carbon is excellent for chlorine, VOCs, many organics, taste, and odor, but is generally not effective for hardness, most simple ions, and some heavy metals without additional treatment steps.[11][2][4]
3. Is activated carbon safe for drinking water and food applications?
Yes, properly manufactured activated carbon approved for food‑grade or drinking water use is considered safe and widely used in beverages, bottled water, and food processing. These activated carbon products meet regulatory standards and are selected to avoid leaching unwanted contaminants into treated water or products.[12][5]
4. Can activated carbon be regenerated or reused?
Many industrial activated carbon filters are designed so the spent activated carbon can be thermally reactivated and reused, restoring a large proportion of its adsorption capacity. Reactivation reduces waste and overall lifecycle cost, making activated carbon filtration more sustainable for large‑scale users.[5][12]
5. Do activated carbon air filters replace HEPA filters?
Activated carbon air filters do not replace HEPA filters because they target different contaminant types. Activated carbon filters adsorb gases, odors, and VOCs, while HEPA filters capture particles such as dust, pollen, and microbes, so many air purifiers combine HEPA and activated carbon media in one system.[13][17]
Citations:
[1](https://puragen.com/uk/insights/the-effectiveness-of-activated-carbon-filters/)
[2](https://extensionpubs.unl.edu/publication/g1489/na/html/view)
[3](https://www.health.state.mn.us/communities/environment/hazardous/topics/gac.html)
[4](https://extension.purdue.edu/extmedia/WQ/WQ-13.html)
[5](https://www.everfilt.com/post/activated-carbon-filtration-media-definition-facts-figures)
[6](https://www.airscience.com/adsorption-vs-absorption-the-difference-for-carbon-filters)
[7](https://www.iso-aire.com/what-is-a-carbon-filter)
[8](https://activatedcarbondepot.com/blogs/news/activated-carbon-filters)
[9](https://joaairsolutions.com/blog/how-does-active-carbon-work/)
[10](https://www.coral.eu/en/insight/i-carboni-attivi-negli-impianti-di-filtrazione-dellaria-industriale/)
[11](https://www.expresswater.com/blogs/watereducation/activated-carbon-vs-other-water-filtration-methods-pros-and-cons)
[12](https://ionexchangeglobal.com/industrial-applications-of-a-water-carbon-filter/)
[13](https://alen.com/blogs/health-benefits/activated-carbon-air-filter)
[14](https://www.calgoncarbon.com/industrial-air-treatment/)
[15](https://tappwater.co/blogs/blog/what-activated-carbon-filters-remove)
[16](https://activatedcarbon.com/applications)
[17](https://rajahfiltertechnics.com/uncategorized/the-science-behind-activated-carbon-how-it-works-and-why-its-effective/)
[18](https://puragen.com/uk/insights/how-does-activated-carbon-filter-water/)
[19](https://www.reddit.com/r/explainlikeimfive/comments/79hmkp/eli5_how_do_activated_carbon_filters_work/)
[20](https://terra-bloom.com/blogs/news/activated-carbon-air-filters-untangling-the-true-from-the-false)
















